[java-live-study] 4주차-제어문
December 08, 2020

조건문(if else)
-
if
if (condition) { /* code */ }condition의 값이true이면 해당 코드가 실행된다. -
if / else
if (condition) { /* code1 */ } else { /* code2 */ }condition의 값이true이면 code1이 실행되고,false이면 code2가 실행된다. -
if / else if / else
if (x == 1) { /* code1 */ } else if (x == 2) { /* code2 */ } else if (x == 3) { /* code3 */ } else { /* code4 */ } /* code5 */x = 1- code1이 실행되고 바로 code5로 넘어간다x != 1,x = 2- code2가 실행되고 바로 code5로 넘어간다x != 1,x != 2,x = 3- code3이 실행되고 code5로 넘어간다x != 1,x != 2,x != 3- code4가 실행된다- 물론
else문 없이if / else만으로 여러 개의 조건을 판별할 수 있지만 실행 속도에 영향을 줄 수 있다.
선택문(switch)
선택문은 조건문과 다르게 변수의 값에 따른 코드 블록을 실행할 수 있다. 여기서 변수는 정수 또는 문자(열)을 가르킨다. 또한 컴파일러에 의해 점프 테이블(jump table)이 생성 및 기록되어 속도 향상을 기대할 수 있다.
위의 if / else if / else 코드를 switch문으로 변경하면 다음과 같다. case마다 break를 넣어주지 않으면 모든 분기를 다 실행할 수 있기 때문에 상황에 맞게 break를 넣어줘야 한다.
switch (x) {
case 1:
/* code1 */
break;
case 2:
/* code2 */
break;
case 3:
/* code3 */
break;
default:
/* code4 */
break; // 생략 가능
}
/* code5 */반복문
여러 반복문을 통해 1~100까지의 합을 구해보자.
while 문
while (조건식) {
실행문
}
int i = 1, sum1 = 0;
while (i <= 100) {
sum1 += i++;
}
int j = 1, sum2 = 0;
while (1) {
sum2 += j;
if (j == 100) break;
j++;
}do-while 문
do {
실행문
} while (조건문);
int i = 1, sum = 0;
do {
sum += i++;
} while (i <= 100);do-while 문은 최소 한 번 이상 실행된다. 세미콜론 주의
for 문
for (초기화식; 조건식; 증감식) {
실행문
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
sum += i;
}
int sum2 = 0;
for (int i = 1, j = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
j += i;
sum2 = j;
}
int sum3 = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; sum3 += i, i++) {
}Enhanced for 문
for (element : array) {
실행문
}
int sum = 0;
int[] arr = new int[100];
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
arr[i] = i + 1;
}
for (int i : arr) {
sum += i;
}-
장점
- 배열의 크기를 몰라도 순회 가능하다.
- 코드가 간결하다.
- 보통 실행 속도가 for문에 비해 약간 빠르다.
- 타입 추론이 가능하다.
-
단점
- 배열의 값을 수정할 수 없다.
- 인덱스에 접근할 수 없다.
- 역순으로 순회할 수 없다.
과제
과제 0. JUnit 5 학습하세요.
과제 1. live-study 대시 보드를 만드는 코드를 작성하세요.
- 깃헙 이슈 1번부터 18번까지 댓글을 순회하며 댓글을 남긴 사용자 체크
- 총 18회 중에 몇 번 참가했는지 참여율 계산(소수점 이하 둘째 자리)
- Github 자바 라이브러리 사용
- (추가) 링크 포함 확인
- (추가) 과제별 참석율 및 평균 참석율
- (추가) 티셔츠 수령 가능 여부
package week4.github;
import org.kohsuke.github.*;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.*;
public class Application {
final private String TOKEN = "<YOUR TOKEN>";
final private String ADDRESS = "whiteship/live-study";
final private float MIN_PERCENTAGE = 80.0f;
private GitHub github;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Application app = new Application();
app.run();
}
void run() throws IOException {
github = new GitHubBuilder().withOAuthToken(TOKEN).build();
GHRepository repo = github.getRepository(ADDRESS);
List<GHIssue> issues = repo.getIssues(GHIssueState.ALL);
int weeks = issues.size();
int latestLockedIssue = 0;
Map<String, List<Integer>> users = new TreeMap<>();
for (int i = weeks - 1, j = 1; i >= 0; i--, j++) {
List<GHIssueComment> comments = issues.get(i).getComments();
if (issues.get(i).isLocked()) {
latestLockedIssue = j;
}
Set<String> nicknames = new HashSet<>();
for (GHIssueComment comment: comments) {
String nickname = comment.getUser().getLogin();
String body = comment.getBody();
if (body.contains("https://") || body.contains("http://")) {
nicknames.add(nickname);
}
}
for (String nickname : nicknames) {
List<Integer> list;
if (users.containsKey(nickname)) {
list = users.get(nickname);
} else {
list = new ArrayList<>();
}
list.add(j);
users.put(nickname, list);
}
}
print(users, weeks, latestLockedIssue);
}
void print(Map<String, List<Integer>> users, int weeks, int latestLockedIssue) {
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
int[] statistics = new int[weeks + 3]; // 통계 저장
statistics[0] = users.size();
// 첫째 줄
str.append("| 참여자 ");
for (int i = 1; i <= weeks; i++) {
str.append("| ").append(i).append("주차 ");
}
str.append("| 참석율 ").append("| 티셔츠 |\n");
for (int i = 1; i <= weeks + 3; i++) {
str.append("| --- ");
}
str.append("|\n");
// 1주차 ~ weeks주차 과제 및 참석율
for (Map.Entry<String, List<Integer>> entry : users.entrySet()) {
String name = entry.getKey();
List<Integer> list = entry.getValue();
str.append("| ").append(name).append(" ");
for (int i = 1, j = 0; i <= weeks; i++) {
str.append("|");
if (j < list.size() && i == list.get(j)) {
str.append("✅");
statistics[i]++;
j++;
}
}
int rest = weeks - Math.max(latestLockedIssue, list.get(list.size() - 1));
float percentage = (float)list.size() / weeks * 100;
statistics[weeks + 1] += percentage * 100;
str.append(" | ").append(String.format("%.2f", percentage));
str.append(" | ");
if ((float)(rest + list.size()) / weeks * 100 < MIN_PERCENTAGE) {
str.append("❌ |\n"); // 불가
} else if (percentage >= MIN_PERCENTAGE) {
str.append("⭕ |\n"); // 확실
statistics[weeks + 2]++;
} else {
str.append("❓ |\n"); // 불확실
}
}
// 마지막 줄
str.append("| ");
for (int i = 0; i < statistics.length; i++) {
if (i == 0 || i == statistics.length - 1) {
str.append(statistics[i]);
} else if (i == statistics.length - 2) {
str.append((float)(statistics[i] / statistics[0]) / 100);
} else {
float percentage = (float)statistics[i] / statistics[0] * 100;
str.append(String.format("%.2f", percentage));
str.append("(").append(statistics[i]).append(")");
}
str.append(" | ");
}
System.out.println(str);
}
}
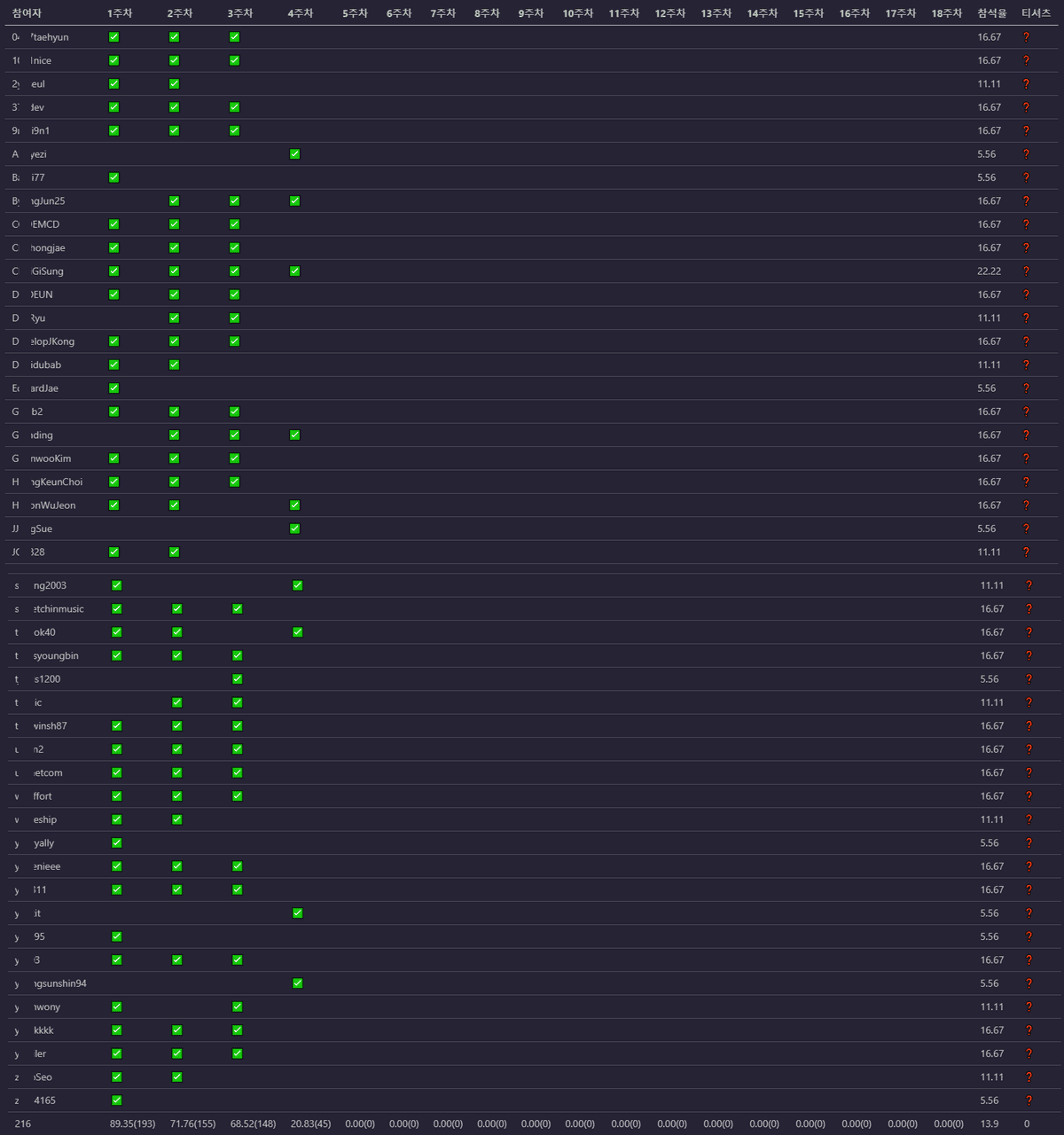
실행 후 출력 결과를 마크다운 파일에 복붙하면 위와 같은 표가 생긴다. 2020-12-08 기준으로 3주차 이슈까지 닫혔기 때문에 아직 모두에게 티셔츠를 얻을 기회가 있다는 것을 알 수 있다.(커트라인 80% 가정)
과제 2. LinkedList를 구현하세요.
- ListNode.java
package week4.linkedlist;
public class ListNode {
private int value;
private ListNode next;
public ListNode() {}
public ListNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public ListNode add(ListNode head, ListNode nodeToAdd, int position) {
ListNode node = head;
if (position < 0) return null;
for (int i = 0; i < position; i++) {
if (node.next == null) break;
node = node.next;
}
nodeToAdd.next = node.next;
node.next = nodeToAdd;
return nodeToAdd;
}
public ListNode remove(ListNode head, int positionToRemove) {
if (positionToRemove < 0 || positionToRemove >= getSize(head)) {
return null;
}
for (int i = 0; i < positionToRemove; i++) {
head = head.next;
}
ListNode deletedNode = head.next;
head.next = head.next.next;
return deletedNode;
}
public boolean contains(ListNode head, ListNode nodeToCheck) {
if (nodeToCheck == null) return false;
while (head != null) {
if (head == nodeToCheck)
return true;
head = head.next;
}
return false;
}
public int getSize(ListNode head) {
int size = 0;
while (head.next != null) {
size++;
head = head.next;
}
return size;
}
public int getValue() {
return this.value;
}
public String toString(ListNode head) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("[");
int size = getSize(head);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
sb.append(head.next.getValue());
if (i != size - 1) sb.append(", ");
head = head.next;
}
sb.append("]");
return sb.toString();
}
}- ListNodeTest.java
package week4.linkedlist;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
class ListNodeTest {
ListNode head = new ListNode();
@BeforeEach
public void makeList() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
head.add(head, new ListNode(i), i);
}
}
@Test
void add() {
assertEquals(10, head.getSize(head));
ListNode nodeToAdd = new ListNode(10);
assertEquals(nodeToAdd, head.add(head, nodeToAdd, 3));
assertNull(head.add(head, new ListNode(100), -1));
}
@Test
void remove() {
assertNull(head.remove(head, -1));
assertNull(head.remove(head, 10));
assertEquals(2, head.remove(head, 2).getValue());
assertEquals(9, head.getSize(head));
}
@Test
void contains() {
ListNode nodeToCheck = new ListNode(10);
head.add(head, nodeToCheck, 0);
head.add(head, new ListNode(20), 1);
assertTrue(head.contains(head, nodeToCheck));
assertFalse(head.contains(head, null));
assertFalse(head.contains(head, new ListNode(20)));
}
}과제 3. Stack을 구현하세요.
- MyStack.java
package week4.stack;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MyStack {
int[] myStack = new int[10];
int size = 0;
public int push(int data) {
if (size >= myStack.length) {
myStack = Arrays.copyOf(myStack, myStack.length * 2);
}
myStack[size++] = data;
return data;
}
public int pop() {
if (empty()) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
} else {
return myStack[--size];
}
}
public boolean empty() {
return size == 0;
}
public int search(int data) {
for (int i = size - 1, j = 0; i >= 0; i--, j++) {
if (myStack[i] == data) {
return j;
}
}
return -1;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
int[] strStack = new int[size];
System.arraycopy(myStack,0,strStack,0,size);
for(int i = size - 1; i >= size / 2; i--){
int temp = strStack[i];
strStack[i] = strStack[size-1-i];
strStack[size-i-1] = temp;
}
return Arrays.toString(strStack);
}
}- MyStackTest.java
package week4.stack;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
@TestMethodOrder(MethodOrderer.OrderAnnotation.class)
class MyStackTest {
static MyStack stack = new MyStack();
@BeforeAll
public static void makeStack() {
for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++) {
assertEquals(i, stack.push(i));
}
}
@Test
@Order(1)
void push() {
assertEquals(20, stack.myStack.length);
assertEquals(11, stack.size);
}
@Test
@Order(2)
void search() {
assertEquals(5, stack.search(5));
assertEquals(-1, stack.search(20));
}
@Test
@Order(3)
void pop() {
for (int i = 10; i >= 0; i--) {
assertEquals(i, stack.pop());
}
assertThrows(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException.class, stack::pop);
}
@Test
@Order(4)
void empty() {
assertTrue(stack.empty());
stack.push(1);
assertFalse(stack.empty());
}
}과제 4. 앞서 만든 ListNode를 사용해서 Stack을 구현하세요.
- ListNodeStack.java
package week4.stack;
import week4.linkedlist.ListNode;
public class ListNodeStack {
static ListNode head = new ListNode();
int size;
void push(int data) {
head.add(head, new ListNode(data), size++);
}
int pop() {
if (size == 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
} else {
return head.remove(head, --size).getValue();
}
}
}- ListNodeStackTest.java
package week4.stack;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import week4.linkedlist.ListNode;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
class ListNodeStackTest {
@Test
void push() {
ListNodeStack stack = new ListNodeStack();
stack.push(100);
stack.push(200);
}
@Test
void pop() {
ListNodeStack stack = new ListNodeStack();
assertThrows(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException.class, stack::pop);
stack.push(10);
assertEquals(10, stack.pop());
}
}과제 5. Queue를 구현하세요.
- MyQueue.java(배열)
package week4.queue;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MyQueue {
int[] myQueue = new int[10];
int left;
int right;
public int push(int data) {
if (right >= myQueue.length) {
myQueue = Arrays.copyOf(myQueue, myQueue.length * 2);
}
return myQueue[right++] = data;
}
public int pop() {
if (left == right) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
} else {
return myQueue[left++];
}
}
}- MyQueueTest.java(배열)
package week4.queue;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
class MyQueueTest {
@Test
void push() {
MyQueue queue = new MyQueue();
queue.push(100);
queue.push(200);
}
@Test
void pop() {
MyQueue queue = new MyQueue();
assertThrows(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException.class, queue::pop);
queue.push(10);
assertEquals(10, queue.pop());
}
}- ListNodeQueue.java(ListNode)
package week4.queue;
import week4.linkedlist.ListNode;
public class ListNodeQueue {
ListNode head = new ListNode();
int size;
public void push(int data) {
head.add(head, new ListNode(data), head.getSize(head));
size++;
}
public int pop() {
ListNode deletedNode = head.remove(head, --size);
if (deletedNode == null) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
} else {
return deletedNode.getValue();
}
}
}- ListNodeQueueTest.java(ListNode)
package week4.queue;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
class ListNodeQueueTest {
@Test
void push() {
ListNodeQueue queue = new ListNodeQueue();
queue.push(100);
queue.push(200);
}
@Test
void pop() {
ListNodeQueue queue = new ListNodeQueue();
queue.push(10);
assertEquals(10, queue.pop());
assertThrows(IndexOutOfBoundsException.class, queue::pop);
}
}