[java-live-study] 8주차-인터페이스
January 06, 2021

인터페이스란
자바에서 인터페이스(interface)는 메서드와 상수를 포함하는 추상 타입이다. 자바의 핵심 개념 중 하나이며, 이를 통해 추상화, 다형성, 그리고 다중 상속을 구현할 수 있다.
다중 상속을 제외한 추상화, 다형성은 추상 클래스로도 구현할 수 있는데 무슨 차이점이 있을까?
-
인터페이스의 모든 메서드는 추상 메서드이고 public 메서드이다.
- 자바8부터 default, static 메서드를 지원한다.
- 자바9부터 private 메서드를 지원한다.
-
추상 클래스를 상속받은 자손 클래스는 자신 또한 추상 클래스가 될 수 있어 모든 추상 메서드를 구현하지 않아도 되지만, 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스는 인터페이스의 모든 추상 메서드를 반드시 구현해야만 한다.
- 추상 클래스의 상속은
extends, 인터페이스의 구현은implements키워드를 사용한다.
- 추상 클래스의 상속은
-
인터페이스는 추상 클래스와 달리 생성자를 가질 수 없다.
- 하지만 둘 다 객체를 생성할 수 없고, 추상 클래스의 생성자는 필드 초기화에 쓰인다.
- 인터페이스는 추상 클래스와 달리 멤버 변수를 가질 수 없다. 상수는 가능.
-
추상 클래스를 포함한 클래스는 단 하나의 추상 클래스만 상속받거나 여러 개의 인터페이스를 구현할 수 있다. (다중 구현)
- 인터페이스는 오직 한 개 이상의 인터페이스를 상속받을 수 있다. (다중 상속)
extends,implements동시에 사용 가능하다.
그렇다면 추상 클래스와 인터페이스 중 무엇을 사용해야 하나?
다중 구현이 가능하고 자바8 이후에 default, static 메서드를 지원하므로 웬만해선 인터페이스를 구현하는 것이 좋다. 단, 인터페이스는 멤버 변수를 가질 수 없기 때문에 이를 잘 판단하여 선택해야겠다.
인터페이스 정의하는 방법
추상 클래스가 A is kind of B라면 인터페이스는 A is able to B이다. 어떠한 기능 및 행위를 하기 위한 메소드를 제공한다는 의미를 강조하기 위해서이다. 따라서 일반적으로 Comparable과 같이 able이 붙곤 한다.
인터페이스 정의의 특징은 다음과 같다.
- 모든 메서드의 접근 제어자는
public이며 생략이 가능하다. - 모든 멤버 변수의 제어자는
public static final이며 생략이 가능하다.
편의상 생략하는 경우가 많은데, 생략하여도 어차피 컴파일 시에 컴파일러가 자동으로 추가한다.
public interface Interface {
public static final int ONE = 1;
public abstract void abstractMethod();
public static void staticMethod() {}
public default void defaultMethod() {}
}인터페이스 구현하는 방법
인터페이스를 구현할 클래스 뒤에 implements키워드를 붙이고 구현부에서 메서드를 오버라이딩하여 구현하면 된다.
public abstract class Animal {
public abstract void eat();
}
public interface Swimmable {
void swim();
}
public interface Flyable {
void fly();
}
public class Shark extends Animal implements Swimmable {
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("shark-eat");
}
@Override
public void swim() {
System.out.println("shark-swim");
}
public void bite() {
System.out.println("shark-bite");
}
}
public class Eagle extends Animal implements Flyable {
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("eagle-eat");
}
@Override
public void fly() {
System.out.println("eagle-fly");
}
public void peck() {
System.out.println("eagle-peck");
}
}
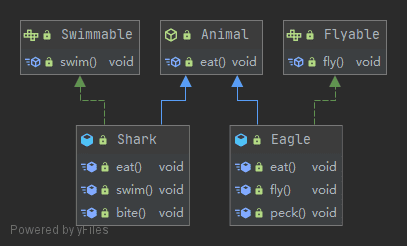
만일 수영도 하고 날 수도 있는 동물인 백조를 추가하려면 어떻게 할까?
인터페이스는 아래와 같이 다중 구현이 가능하다.
이하 어노테이션은 생략하도록 하겠다.
public class Swan extends Animal implements Flyable, Swimmable{
public void eat() {
System.out.println("swan-eat");
}
public void fly() {
System.out.println("swan-fly");
}
public void swim() {
System.out.println("swan-swim");
}
}
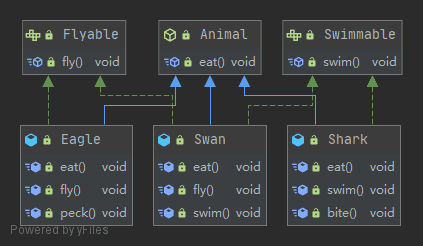
인터페이스 레퍼런스를 통해 구현체를 사용하는 방법
앞서 말했듯이 인터페이스는 객체를 생성할 수 없다. 허나 인터페이스도 다형성이 적용되기 때문에 구현한 인터페이스의 타입으로 형변환이 가능하다. 우리가 알고있는 상속과 같은 메커니즘이다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Flyable flyable = new Eagle();
Swimmable swimmable = new Shark();
flyable.fly(); // eagle-fly
swimmable.swim(); // shark-swim
((Eagle)flyable).peck(); // eagle-peck
((Shark)swimmable).bite(); // shark-bite
}
}인터페이스 상속
인터페이스도 클래스와 마찬가지로 상속이 가능하다. 다른 점은 클래스의 최고 조상이 Object이지만 인터페이스의 최고 조상은 없고, 한 개 이상의 인터페이스를 상속받을 수 있어 다중 상속이 가능하다.
위의 코드에서 Animal추상 클래스를 인터페이스로 바꾸고 Bird인터페이스를 추가하였다.
public interface Animal {
public abstract void eat();
}
public interface Flyable {
void fly();
}
public interface Swimmable {
void swim();
}
public interface Bird extends Flyable, Animal {
int LEGS = 2;
void peck();
}
public class Shark implements Swimmable, Animal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("shark-eat");
}
public void swim() {
System.out.println("shark-swim");
}
public void bite() {
System.out.println("shark-bite");
}
}
public class Eagle implements Bird {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("eagle-eat");
}
public void fly() {
System.out.println("eagle-fly");
}
public void peck() {
System.out.println("eagle-peck");
}
}
public class Swan implements Bird, Swimmable {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("swan-eat");
}
public void fly() {
System.out.println("swan-fly");
}
public void swim() {
System.out.println("swan-swim");
}
public void peck() {
System.out.println("swan-peck");
}
}
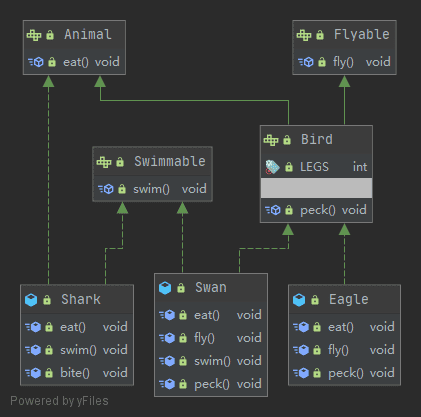
인터페이스의 default 메서드, 자바8
자바8부터 default 메서드를 지원한다.
기존의 추상 메서드는 같은 구현부라 하더라도 각 클래스에서 구현을 해줘야했다. 그럼 변경이 있을 때마다 모두 수정해줘야 하는 번거로움이 생겼다. 따라서 효율적인 유지보수를 위해 default 메서드를 활용할 수 있다. 참고로 default는 생략할 수 없다.
위의 예제에서 상어와 백조의 수영법이 같다고 하면 어떻게 코드를 변경할 수 있을까?
public interface Swimmable {
default void swim() {
System.out.println("swim");
}
}
public class Shark implements Swimmable {}
public class Swan implements Swimmable {}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Swan swan = new Swan();
Shark shark = new Shark();
swan.swim(); // swim
shark.swim(); // swim
}
}⚠️ 여러 인터페이스의 메서드 시그니처가 같다면 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스에서 default 메서드를 오버라이딩 해야 한다.
⚠️ 조상 클래스의 메서드 시그니처와 구현한 인터페이스의 default 메서드 시그니처가 같다면 조상 클래스의 메서드가 상속된다.
인터페이스의 static 메서드, 자바8
자바8부터 static 메서드를 지원한다.
인터페이스에 접근하여 사용하는 메서드이다. 그렇기에 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스에서 static 메서드를 오버라이딩 할 수 없다. Bird인터페이스에서 새의 다리 수를 가져오는 static메서드를 정의하고 호출해보자.
public interface Bird extends Flyable, Animal {
int LEGS = 2;
default void peck() {
System.out.println("bird-peck");
}
static int getLegs() {
return LEGS;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Swan swan = new Swan();
swan.peck(); // swan-peck
System.out.println(Bird.getLegs()); // 2
}
}인터페이스의 private 메서드, 자바9
자바9부터 private 메서드를 지원한다.
private 메서드를 사용함으로써 정보 은닉이 가능해진다. 다른 메서드는 외부에서 접근할 수 있는데 반해 private 메서드는 인터페이스에서만 사용 가능하다.
public interface Bird extends Flyable, Animal {
int LEGS = 2;
default void peck() {
System.out.println("bird-peck");
}
default void info() {
System.out.println("bird has " + getLegs() + "legs");
}
private int getLegs() {
return LEGS;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Swan swan = new Swan();
swan.peck(); // swan-peck
swan.info(); // bird has 2legs
}
}